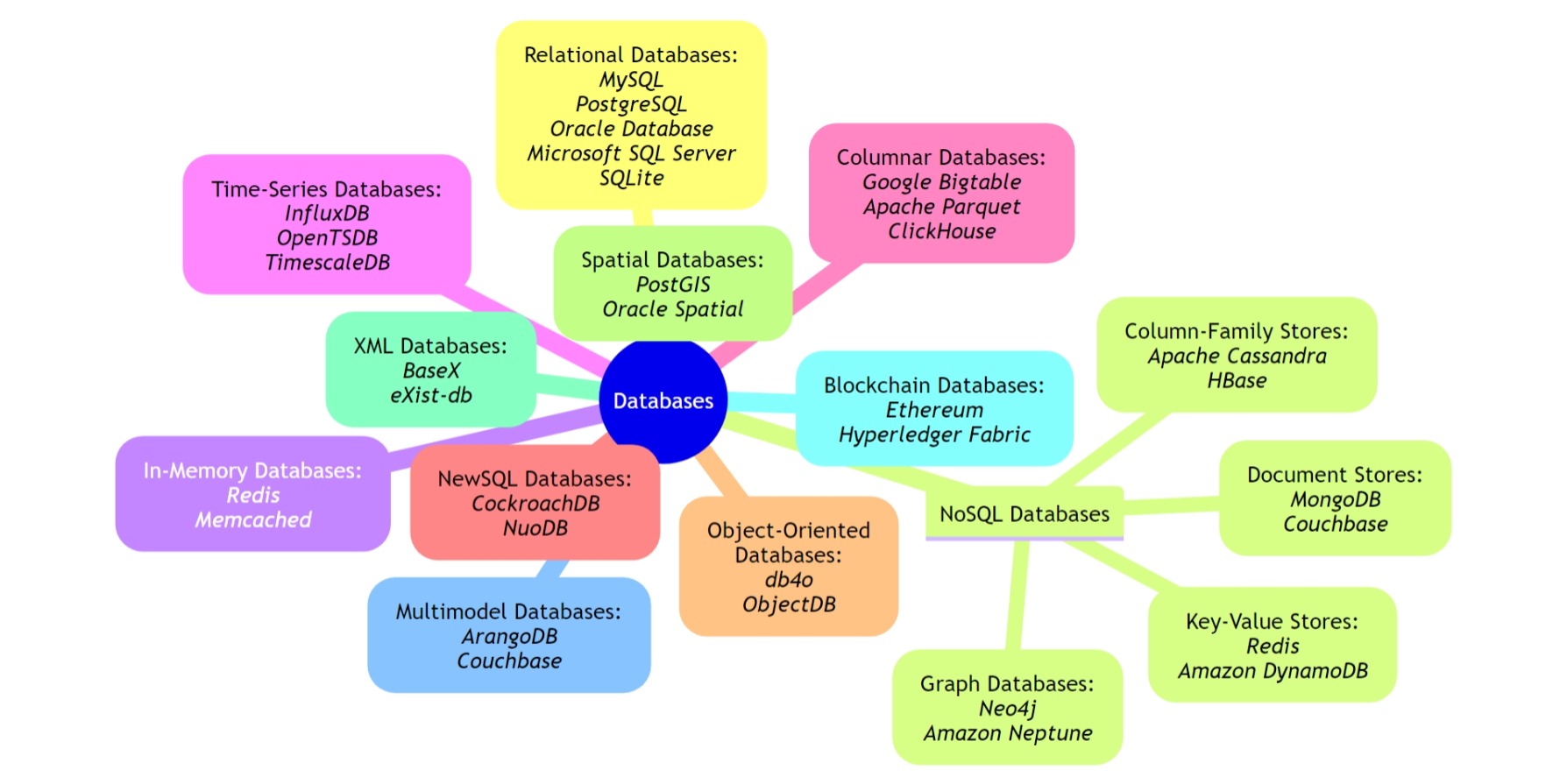
Various Types of Databases
In today’s data-driven world, understanding the different types of databases is crucial for building robust and efficient applications. Let’s dive into some of the key database categories and their real-world examples.
Relational Databases (RDBMS): These are the most traditional and widely used types of databases. They organize data into structured tables with rows and columns, where each row represents a record and each column represents a field.
NoSQL Databases: NoSQL databases are designed to handle unstructured, semi-structured, or rapidly changing data. They diverge from the traditional tabular relations of relational databases and come in various forms:
- Document Stores: Store data in documents, often in JSON or XML formats.
- Key-Value Stores: Store data as key-value pairs.
- Column-Family Stores: Store data in column families, which are columns grouped together.
- Graph Databases: Store data in nodes and edges to represent complex relationships.
In-Memory Databases: These databases store data in system memory (RAM) rather than on disk, allowing for faster data access and retrieval.
Time-Series Databases: Designed to handle and manage time-stamped data, often generated from sensors, IoT devices, financial applications, and more.
Columnar Databases: These databases store data in columns rather than rows, which is particularly efficient for analytical queries and data warehousing.
NewSQL Databases: These databases aim to combine the advantages of traditional relational databases with the scalability and performance improvements offered by NoSQL databases.
Object-Oriented Databases: These databases are designed to work with object-oriented programming languages and store objects, classes, and relationships directly.
Spatial Databases: Designed to store and manage spatial or geographic data, allowing for the efficient storage and querying of location-based information.
XML Databases: These databases are optimized for storing and querying XML data.
Blockchain Databases: Used for storing data in a tamper-evident and decentralized manner using blockchain technology.
Multimodel Databases: These databases support multiple data models within a single database, allowing you to store and query data in various ways.
Remember, there are possibilities of other emerging categories too! Each type has its own strengths, making the choice crucial to your project’s success.
Stay curious, and keep exploring the evolving world of databases! 🔍💡