Integrating Cybersecurity into Product Development - A Step-by-Step Approach
Cybersecurity is no longer an optional feature in the digital age. It is a necessity for any product that interacts with data, networks, or users. As cyber threats become more sophisticated and diverse, product developers need to adopt a proactive approach to embedding cybersecurity practices into their development processes. This will not only enhance the protection of their products against potential attacks, but also improve their quality, performance, and customer satisfaction.
In this blog post, I will explore some of the insights from Arun Arora’s book “Fast Times: How Digital Winners Set Direction, Learn, and Adapt”, which shows how cybersecurity can be a part product development. He has provided a step-by-step approach to integrate cybersecurity into product development, from architecture and design to testing and deployment. Based on that we will also discuss practical examples of how this approach can be implemented in real-world scenarios.
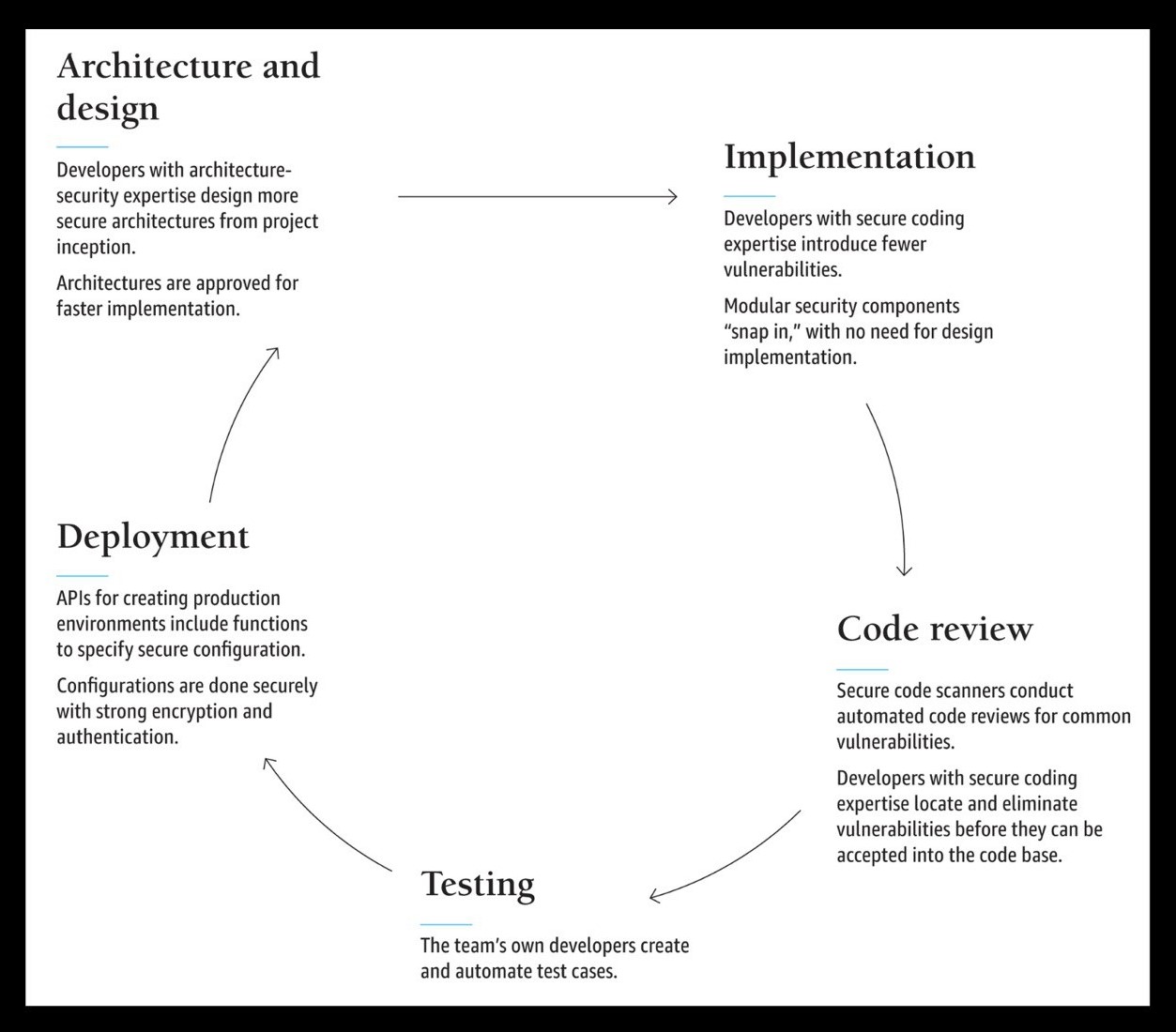
1. Architecture and Design: Building a Secure Foundation
The first step in integrating cybersecurity into product development is to design a secure project architecture from the beginning. This involves having developers with architecture-security expertise who can identify the security requirements and objectives of the product, as well as the potential threats and risks it may face. These developers can then design a secure architecture that minimizes the attack surface and maximizes the defense-in-depth of the product.
Having a secure architecture approved early in the development process has several advantages. First, it provides a clear and consistent vision for the product’s security goals and strategies. Second, it facilitates faster and smoother implementation, as developers can follow the predefined security guidelines and standards. Third, it reduces the likelihood of introducing vulnerabilities or errors that may compromise the product’s security later on.
For example, consider a product that involves collecting and processing sensitive user data, such as a health app. A secure architecture for this product would include features such as data encryption, access control, audit logging, and backup mechanisms. These features would ensure that the user data is protected from unauthorized access, modification, or loss, both in transit and at rest.
2. Implementation: Coding with Security in Mind
The second step in integrating cybersecurity into product development is to code with security in mind. This means having developers with secure coding expertise who can apply best practices and techniques to avoid introducing vulnerabilities or weaknesses during implementation. These developers can also leverage modular security components that seamlessly integrate into the development process and provide ready-made solutions for common security challenges.
Using modular security components has several benefits. First, it allows developers to “snap in” security features without disrupting the design or functionality of the product. Second, it saves time and resources, as developers do not have to reinvent the wheel or rely on third-party libraries that may have unknown or untrusted origins. Third, it ensures consistency and compatibility across different platforms and environments.
For example, consider a product that involves communicating with external services or APIs, such as a chatbot. A modular security component for this product would include features such as secure communication protocols, certificate validation, and message authentication. These features would ensure that the communication between the product and the external services or APIs is secure and reliable.
3. Code Review: Identifying and Eliminating Vulnerabilities
The third step in integrating cybersecurity into product development is to identify and eliminate vulnerabilities through code review. This involves using secure code scanners for automated code reviews and vulnerability detection. These scanners can scan the codebase for common security flaws or bugs, such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting, or buffer overflow. They can also provide recommendations or fixes for resolving these issues.
In addition to using secure code scanners, developers with secure coding expertise play a critical role in identifying and resolving vulnerabilities before they become part of the codebase. These developers can perform manual code reviews and peer reviews to verify the quality and security of the code. They can also use tools such as penetration testing tools or frameworks to validate the functionality and behavior of the code.
Performing code review has several benefits. First, it prevents security issues from reaching production environments where they may cause damage or harm to the product or its users. Second, it improves the maintainability and readability of the code by removing unnecessary or redundant code. Third, it fosters a culture of security awareness and accountability among developers.
For example, consider a product that involves processing user input or queries, such as a search engine. A code review for this product would include features such as input validation, output encoding, and error handling. These features would ensure that the user input or queries are properly sanitized and processed, and that any errors or exceptions are handled gracefully and securely.
4. Security Testing: Ensuring Robust Security Measures
The forth step in integrating cybersecurity into product development is to ensure robust security measures through testing. This involves creating and automating test cases for security that cover different aspects of the product, such as functionality, performance, usability, and compatibility. These test cases can also simulate different scenarios or conditions that may affect the product’s security, such as network latency, user behavior, or malicious attacks.
Security testing is an iterative process that is integrated into the overall development process. It involves running the test cases at different stages of the development cycle, such as before and after code review, deployment, or release. It also involves analyzing the test results and feedback to identify and address any issues or gaps in the product’s security.
It has several benefits. Such as, it ensures that the product meets the security expectations and requirements of the stakeholders and end-users. Second, it verifies that the product functions correctly and securely under different circumstances and environments. Third, it contributes to continuous improvement of the product’s security measures by identifying and resolving any weaknesses or vulnerabilities.
For example, consider a product that involves providing online services or transactions, such as a banking app. A security testing for this product would ensure that the online services or transactions are secure and reliable, and that they work well across different devices and browsers.
5. Deployment: Securely Configuring Production Environments
The fifth step in integrating cybersecurity into product development is to securely configure production environments. This involves creating production environments that have configurable security settings that match the security requirements and objectives of the product. These can also enable developers to automate the deployment process and ensure that the security configurations are applied consistently across different instances of the product.
Using secure configurations with strong encryption and authentication has several benefits. First, it enhances the overall security posture of the product by preventing unauthorized access or tampering with its data or functionality. Second, it reduces the risk of exposing sensitive information or credentials that may compromise the product’s security or integrity. Third, it improves the performance and scalability of the product by optimizing its resource utilization and availability.
For example, consider a product that involves hosting web applications or services on cloud platforms, such as a e-commerce site. A secure configuration for this product would include features such as HTTPS encryption, SSL certificates, and API keys. These features would ensure that the web applications or services are securely delivered to the end-users and protected from malicious actors.
6. Iterative Process: Enhancing Security Across Development Cycles
The final step in integrating cybersecurity into product development is to enhance security across development cycles through an iterative process. This means repeating the previous steps for each new feature or update of the product, as well as for any changes or modifications in the security requirements or objectives. This also means incorporating feedback and lessons learned from each iteration to improve the product’s security posture.
The iterative process has several benefits. First, it maintains and enhances the product’s security posture by keeping up with the evolving threats and risks in the cyber landscape. Second, it adapts and aligns the product’s security measures with the changing needs and expectations of the stakeholders and end-users. Third, it creates a competitive advantage for the product by delivering superior security value and quality.
For example, consider a product that involves integrating with other products or platforms, such as a social media app. An iterative process for this product would include features such as architecture review, code review, configuration review, and security testing review. These features would ensure that the integration with other products or platforms is secure and seamless, and that any new or existing vulnerabilities are identified and eliminated.
Conclusion
Integrating cybersecurity into product development is not a one-time effort but a continuous process. It requires a step-by-step approach that covers all aspects of the development cycle, from architecture and design to testing and deployment. It also requires a team of developers with architecture-security expertise, secure coding expertise, and secure deployment expertise who can implement best practices and techniques for creating secure products.
By following this approach, product developers can achieve several benefits, such as enhanced product security, reduced vulnerabilities, improved customer trust, and increased competitive edge. They can also create products that are not only functional and user-friendly but also secure and resilient against cyber threats.
Happy Learning…