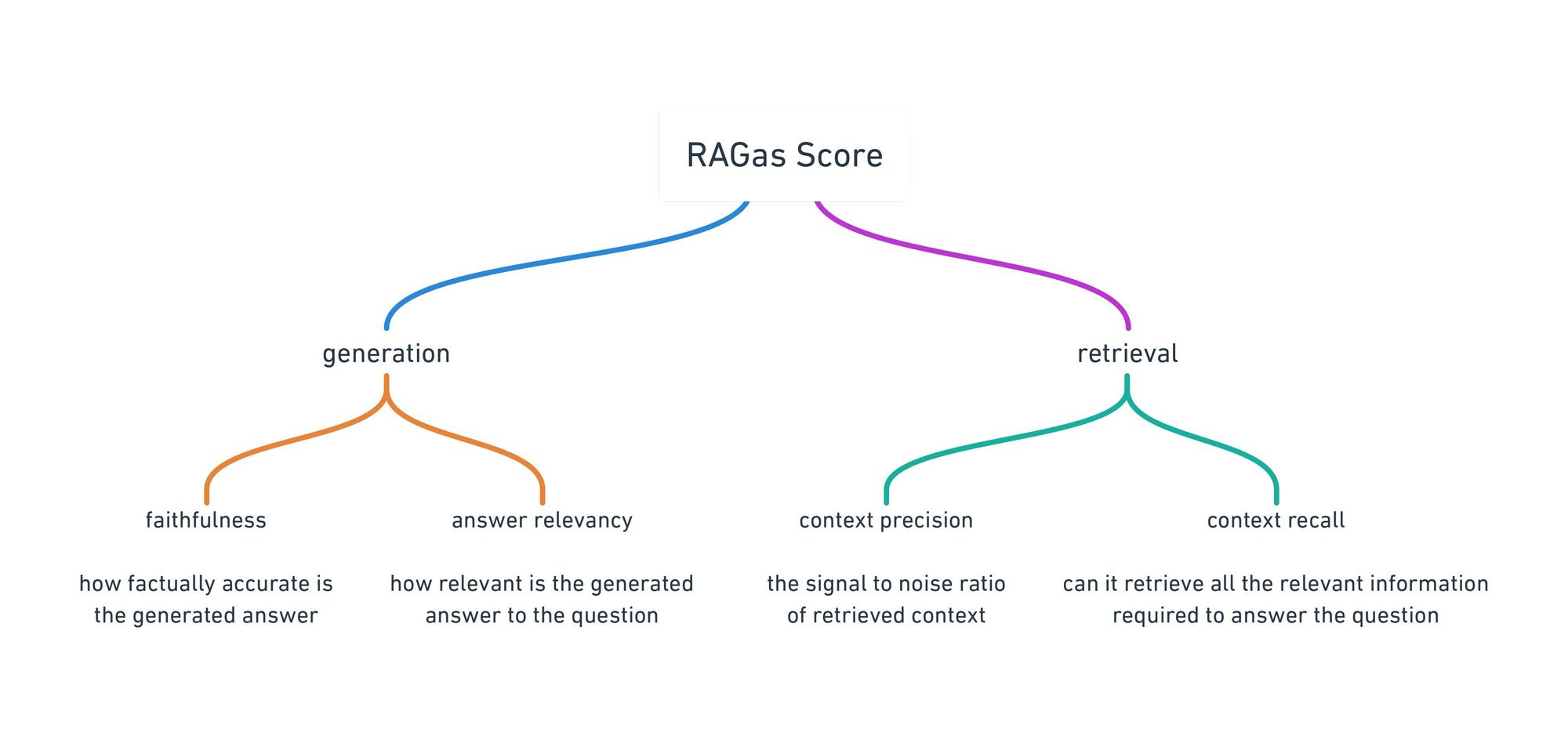
Evaluation of Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) Systems
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) is a powerful technique that enhances large language models (LLMs) by incorporating external knowledge sources. This allows LLMs to access and reference authoritative knowledge bases or internal repositories before generating responses, resulting in outputs based on specific domains or contexts. RAG is a cost-effective solution for improving LLM performance for various applications, as it doesn’t require retraining the model.
However, RAG systems also present challenges, such as retrieving the most relevant knowledge, avoiding hallucinations (responses inconsistent with the retrieved context), and efficiently integrating retrieval and generation components. These challenges highlight the importance of monitoring and evaluating generative AI applications powered by RAG.
So, you want to know the problem before the customer tell you, right?
Why RAG Evaluation Matters?
- Assessing Effectiveness and Reliability: Evaluation helps understand how well RAG models utilize external knowledge, retrieve relevant information, and generate outputs in real-world scenarios.
- Identifying Issues: It can uncover potential biases, hallucinations, inconsistencies, or factual errors that may arise from integrating external sources or suboptimal prompt engineering.
- Improving Performance: By identifying areas for improvement, evaluation can lead to enhanced performance, reduced costs, and better user experiences.
Several Challenges of RAG Evaluation
- Lack of Ground Truth References: In many open-ended generation tasks, there’s no single correct answer, making it difficult to apply standard evaluation metrics.
- Faithfulness Evaluation: Ensuring that generated output is faithful to the retrieved context and doesn’t contain hallucinations is a complex task.
- Context Relevance Assessment: Automatically assessing the relevance of retrieved context to the input prompt is an ongoing challenge.
- Balancing Factuality and Coherence: Striking the right balance between factual accuracy and natural language fluency is difficult.
- Compounding Errors and Traceability: Errors can originate from both retrieval and generation components, making diagnosis and traceability challenging.
- Human Evaluation Challenges: While human evaluation is possible, it’s expensive, subjective, and may not scale well.
Overcoming Challenges and Ensuring Reliability
- Developing Robust Metrics: Researchers are actively working on creating automated metrics that can quantitatively assess the reliability of RAG systems at scale.
- Utilizing LLM Judges: Leveraging language models with reasoning capabilities as judges can help automate the evaluation process.
- Continuous Monitoring and Optimization: Implementing observability tools and feedback loops allows for continuous monitoring and optimization of RAG systems.
- Human-in-the-Loop: Maintaining human oversight is crucial for aligning AI systems and their evaluation mechanisms with intended uses and objectives.
By focusing on robust evaluation methodologies, we can optimize the RAG systems, from question answering to content generation.
References: